Understanding ARP Protocol: How it Works and Why it Matters?
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a crucial component of networking that allows network devices to map an IP address to a MAC address. In this article, we will explain how ARP works, its importance in networking, and how it can be used to troubleshoot network issues.
What is ARP Protocol?
ARP is defined in RFC 826. Switches use ARP to discover the physical address of another device on the network. It operates at the Data Link Layer of the OSI model and is used to map an IP address to a MAC address. This mapping is necessary because while IP addresses are used to route packets between networks (which is the job of a router), MAC addresses are used to actually deliver the packets to the correct device on a LAN (which is the job of a switch)
How ARP Works
When a device wants to communicate with another device on a LAN, it first checks its ARP cache (a table stored on the device that contains recently looked up IP-to-MAC address mappings) to see if it already has the necessary information. If the mapping is not found in the cache, the device sends an ARP broadcast packet to the network, asking for the MAC address associated with the IP address of the destination device.
All devices on the LAN will receive the ARP broadcast packet, but only the device with the matching IP address will respond with its MAC address. The requesting device then stores this mapping in its ARP cache for future use.
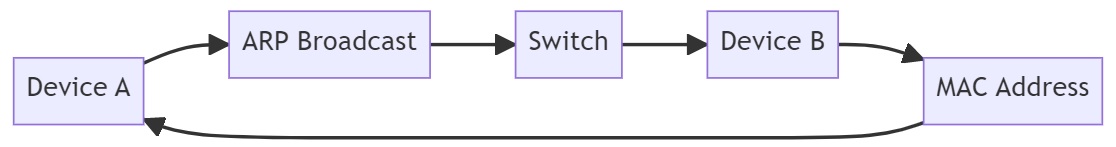
As the above diagram illustrates, when Device A wants to communicate with Device B, it sends an ARP broadcast which is received by the Network Switch. The switch then looks up the IP-to-MAC address mapping in its ARP table, and if it has the mapping it forwards the packet to the correct port. If it doesn’t have the mapping it floods the packet to all ports except the incoming port to find the correct device. Once the correct device responds with its MAC address, the switch updates its ARP table and forwards the packet to the correct port, enabling communication between Device A and Device B.
The Importance of ARP
ARP plays a crucial role in enabling communication between devices on a LAN. Without ARP, devices would not be able to determine the physical addresses of other devices, and thus would not be able to deliver packets to them. This would effectively disable communication between devices on the same LAN.
Additionally, ARP is also used in security attacks such as ARP spoofing, where an attacker can map their own MAC address to the IP address of another device on the network, allowing them to intercept network traffic intended for that device.
Troubleshooting with ARP
If you are experiencing network issues, ARP can be a valuable tool for troubleshooting. By checking the ARP cache on a device, you can determine if the device is able to correctly map IP addresses to MAC addresses. Additionally, if you suspect ARP spoofing, you can check for discrepancies between the ARP cache and the actual physical addresses of devices on the network.
Role of Network Switches in ARP
Network switches play a critical role in ARP as they are responsible for maintaining and updating the ARP table. As devices on the network communicate with each other, the switch updates its ARP table with the correct IP-to-MAC address mappings. This allows for efficient communication between devices on the LAN as the switch can quickly look up the necessary information in its ARP table instead of sending out broadcast packets.
Conclusion
ARP is a fundamental protocol that enables the communication between devices on a LAN. It is important to understand how it works and its role in network security to ensure proper network functioning and troubleshoot issues when they arise. Network switches play a critical role in maintaining and updating the ARP table, allowing for efficient communication on the LAN.