What is 5G Network?
In this article, we’ll scratch the surface of what will be going on in the field of mobile communication in the years to come. So, what is a 5G network?
The 5G network is the 5th generation of mobile network technology. 5G mobile standard will bring low latency (1ms or less), high-speed broadband internet (up to 10 Gbps per user, in theory), improved battery life, …
All that will result in significant improvement in customer experience such as faster download, wider multimedia options, better connectivity, high-quality sound, and HD video will be sent to another mobile phone without loss of quality.
Those are the benefits in terms of human communications, but let’s be honest there is no big difference would you receive an e-mail in 5 seconds or 30 seconds, so to us humans delay (latency) is not so critical. With that being said let’s say something about even more important goal of 5G networks which is to support massive machine-to-machine communications and to provide high-reliability service for mission-critical applications.
Some examples of industries which the 5G network will transform are:
- Medicine
- Emergency communications
- Smart cities
- Traffic
- Factories of the future
- Internet of things
To achieve all the benefits that the 5G network will bring network infrastructure must be improved.
5G Network Architecture
5G Frequency Bands and Radio Access Network
- < 1 GHz – Long-range frequencies
- Between 1 GHz and 6 GHz – Mobile broadband and mission-critical usage
- > 6 GHz – short range but high throughput
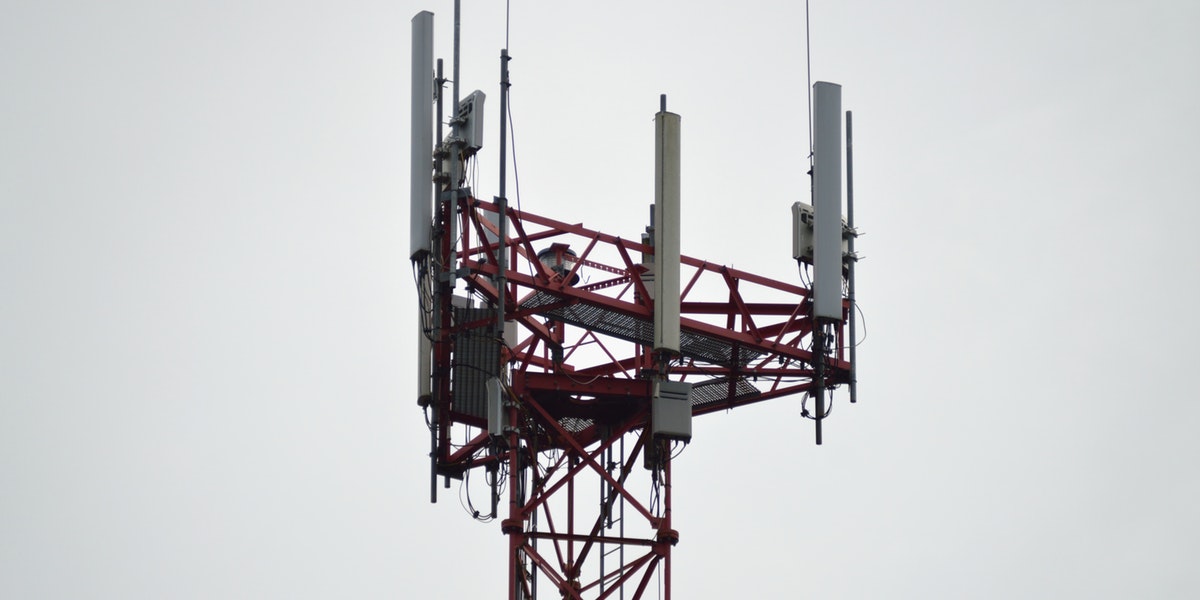
4G (LTE) and 5G networks will be able to work “together”. Users will be able to use 4G, 5G, and Wi-Fi at the same time. Higher antenna density (cell towers) will be needed for 5G to provide fast speeds and low latency to end users. The result of that will be that the 5G network will be 20 times faster than 4G. 5G antennas will be MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) antennas that can send and receive more data simultaneously. MIMO technology enables more people to simultaneously connect to the network and still maintain high throughput. The physical size of 5G antennas will be similar to 3G and 4G base station antennas.
Core Network
In the core network, better fixed and mobile convergence will happen in order to be able to provide a far greater amount of bandwidth. Also core network will be a part of the network that needs to provide low latency.
To support 5G backhaul and edge computing, many providers deploy Metropolitan Area Networks that connect cell sites to core networks.
Advantages of 5G Network
- High throughput => Faster speeds to the user
- Low latency
- Longer battery life
Disadvantages of a 5G Network
- No backwards compatibility (with older devices) => Users have to buy a new device
- Higher costs for service providers (investments in infrastructure, engineers, maintenance, …)
- Risk of possible 5G radio spectrum saturation (because of more devices per channel)
The interactive Ookla 5G Map can be found here.